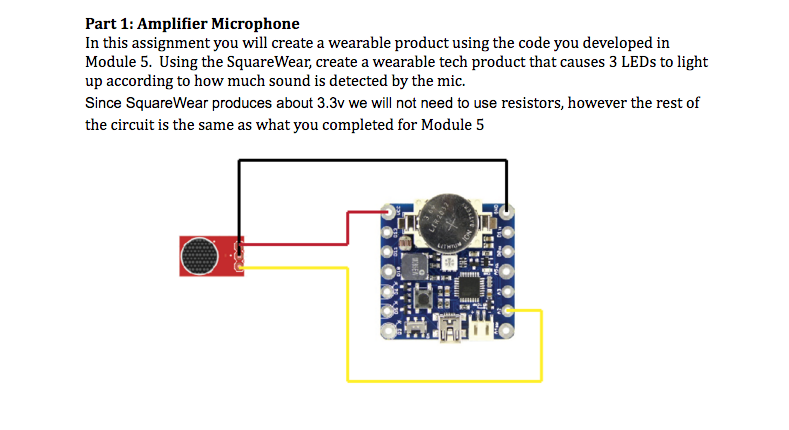
Assignment 6: Code Review and LEDs Responding to Sound
Goal of this Assignment: Practice using amp mic.Assignment 6: LEDs Responding to Sound
Assignment: Exploring Sensors Lesson
/* MAX4466 (adafruit mic) Written by Shani Mensing, edited by Audrey St. John Circuit: microphone VCC connected to 3.3V, OUT to analog input A0 */ // hook up the out of the mic to analog input A0 #define MIC_IN A0 // Sample window width in milliseconds (50 ms = 20Hz) int sampleWindow = 50; /** * Initialization code **/ void setup() { // open serial port and set data rates to 9600 bps (bits-per-second) // this lets us communicate to/from the arduino Serial.begin(9600); pinMode( MIC_IN, INPUT ); } /** * Main program loop happens constantly. **/ void loop() { // read the analog sensor as volts double soundSensed = sampleSoundPeak(); // print it out Serial.println(soundSensed); } /////////////// Our own methods /** * Sense biggest input difference are being input from the analog MIC sensor * over a certain "window" of time. * Values returned are in the range 0 - 1024. **/ double sampleSoundPeak() { // record start time double startMillis = millis(); // this will be the highest peak, so start it very small int signalMax = 0; // this will be the lowest peak, so start it very high int signalMin = 1024; // will hold the current value from the microphone int sample; // collect data for 50 ms while ( (millis() - startMillis) < sampleWindow ) { // read a value from mic and record it into sample variable sample = analogRead( MIC_IN ); // toss out spurious readings if (sample < 1024) { // if the current sample is larger than the max if (sample > signalMax) { // this is the new max -- save it signalMax = sample; } // otherwise, if the current sample is smaller than the min else if (sample < signalMin) { // this is the new min -- save it signalMin = sample; } } } // now that we've collected our data, // determine the peak-peak amplitude as max - min int peakDifference = signalMax - signalMin; // give it back to the caller of this method return peakDifference; }