Assignment 3: Pseudocode and Capacitive Touch
Goal of this Assignment: Practice creating Pseudocode and using ArduinoAssignment 1: Soft Circuit DIY Doll Document Download
Module: Intro to Arduino and Basics in Pseudocode Lesson
GoalsPseudocode
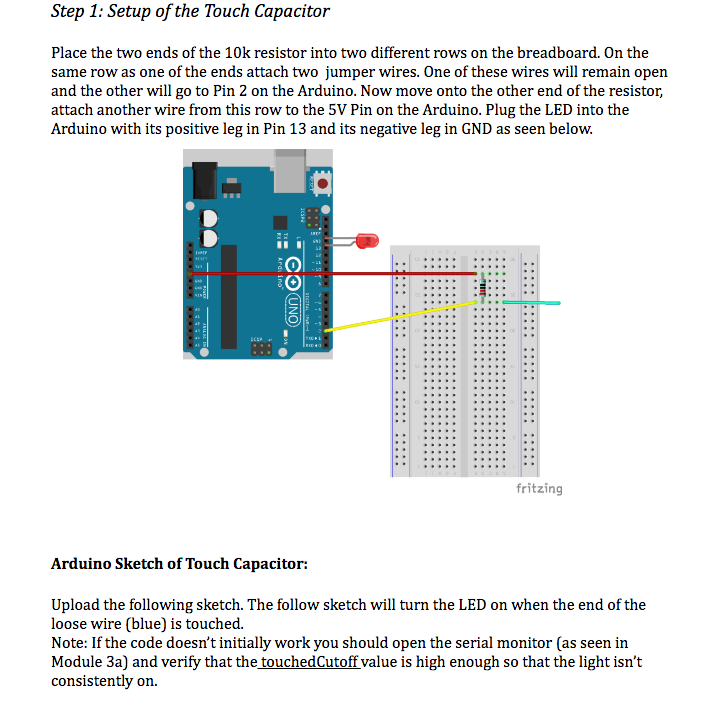
Capacitive Touch
/** * Capacitive touch example, adapted by Eva Snyder from * http://www.instructables.com/id/Turn-a-pencil-drawing-into-a-capacitive-sensor-for/ **/ // Pin for the LED int LEDPin = 13; // Pin to connect to your conductive sensor // (paperclip, conductive paint/fabric/thread, wire) int capSensePin = 2; // This is how high the sensor needs to read in order // to trigger a touch. You'll find this number // by trial and error, or you could take readings at // the start of the program to dynamically calculate this. // If this is not sensitive enough, try a resistor with more ohms. int touchedCutoff = 20; void setup(){ Serial.begin(9600); // Set up the LED pinMode(LEDPin, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(LEDPin, LOW); } void loop(){ //If the capacitive sensor reads above a certain threshold, //turn on the LED if (readCapacitivePin(capSensePin) > touchedCutoff { digitalWrite(LEDPin, HIGH); } else { digitalWrite(LEDPin, LOW); } // Every 500 ms, print the value of the capacitive sensor if ( (millis() % 500) == 0){ Serial.print("Capacitive Sensor reads: "); Serial.println(readCapacitivePin(capSensePin)); } } //------------------------------Only Modify Above this Line----------------------- // readCapacitivePin // Input: Arduino pin number // Output: A number, from 0 to 17 expressing // how much capacitance is on the pin // When you touch the pin, or whatever you have // attached to it, the number will get higher // In order for this to work now, // The pin should have a resistor pulling // it up to +5v. uint8_t readCapacitivePin(int pinToMeasure){ // This is how you declare a variable which // will hold the PORT, PIN, and DDR registers // on an AVR volatile uint8_t* port; volatile uint8_t* ddr; volatile uint8_t* pin; // Here we translate the input pin number from // Arduino pin number to the AVR PORT, PIN, DDR, // and which bit of those registers we care about. byte bitmask; if ((pinToMeasure >= 0) && (pinToMeasure <= 7)){ port = &PORTD; ddr = &DDRD; bitmask = 1 << pinToMeasure; pin = &PIND; } if ((pinToMeasure > 7) && (pinToMeasure <= 13)){ port = &PORTB; ddr = &DDRB; bitmask = 1 << (pinToMeasure - 8); pin = &PINB; } if ((pinToMeasure > 13) && (pinToMeasure <= 19)){ port = &PORTC; ddr = &DDRC; bitmask = 1 << (pinToMeasure - 13); pin = &PINC; } // Discharge the pin first by setting it low and output *port &= ~(bitmask); *ddr |= bitmask; delay(1); // Make the pin an input WITHOUT the internal pull-up on *ddr &= ~(bitmask); // Now see how long the pin to get pulled up int cycles = 16000; for(int i = 0; i < cycles; i++){ if (*pin & bitmask){ cycles = i; break; } } // Discharge the pin again by setting it low and output // It's important to leave the pins low if you want to // be able to touch more than 1 sensor at a time - if // the sensor is left pulled high, when you touch // two sensors, your body will transfer the charge between // sensors. *port &= ~(bitmask); *ddr |= bitmask; return cycles; }Modify Code